When you start learning basic English, the first thing you learn is tenses. However, they might look simple, even though they are not. The complexity of tenses in English can make anyone with a good hold over the language nervous.
Tenses denote the time when the event took place. The different tenses are noted with the help of their verb forms. In simple terms, verb tenses are additions or changes to verbs to identify the time of the action, whether it took place in the present, past, or future.
This falls under the basic grammar rules and is one of the most essential skills for communicating with people, both in written form and verbally. So, to convey the message, you need to have a sound knowledge of tenses in English.
What Are Tenses In English?
Tense is a verb form that expresses the time of the action or incident. It lets us know about the time when something happened, when the event took place, or when someone did something. The three main types of tenses in English are past, present, and future.
According to Merriam-Webster, tens are “a distinction of form in a verb to express distinctions of time or duration of the action or state it denotes.”
According to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, tense is “any of the forms of a verb that may be used to show the time of the action or state expressed by the verb.”
Collins Dictionary says, “The tense of a verb group is its form, which usually shows whether you are referring to past, present, or future time.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, tense is “any of the forms of a verb which show the time at which an action happened.”
As mentioned earlier, the three main forms of tense are present tense, past tense, and future tense.
Different Types Of Tense
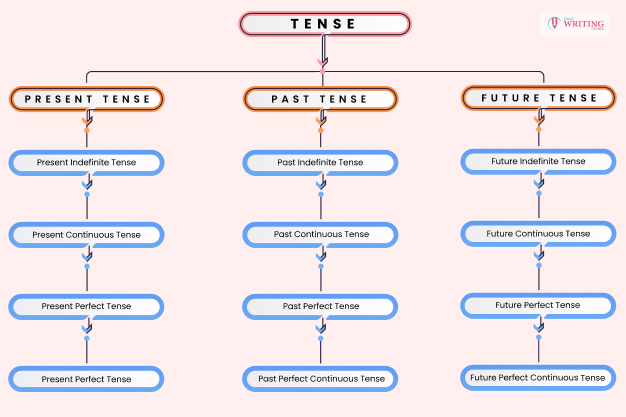
As mentioned earlier, there are three different types of tense: past, present, and future. Let’s examine how these work.
Past Tense
The past tense is specifically used to describe an event or an activity that has taken place before or has happened in the past state of being. It often needs to mark a time when the action or event took place.
Structural formula: Subject + verb (second form) + object
Examples
- I met him yesterday.
- She bought him a new phone last week.
- He expired last week in an accident.
- He wrote the papers for months for the final dissertation.
- I wish I could go on the trip with them.
Present Tense
Present tense or simple present tense is again among the basic English tenses. It is used to talk about something which is currently happening. It is something that is performed out of habit or a state which currently exists.
Structural formula: Subject + verb (s/es) + object
Examples:
- He lives in Paris.
- Bella drives a cab for a living.
- She does a lot for her family, and they do not even acknowledge it.
- She writes a lot to meet her daily target.
- She feels drained after coming from a long day of work.
Future Tense
The future tense is another form of verb tense that is used for describing an action or an event that has not happened yet or is about to happen in the near future.
Structural formula: Subject + will/shall + verb (s/es) + object
Examples:
- She will be here soon.
- HR will be conducting the interview from tomorrow onwards.
- He will be doing a lot of work this week.
- She will be drained after the long journey.
- Jen will be leaving for Paris in the coming week.
Additional Aspects Of Tenses

Along with the basic past, present, and future tense, there are some other aspects of tense that you should be aware of. Here are those aspects mentioned.
Simple Tense
Simple tense is a grammatical aspect that refers to the normal tense forms of past, present, and future. It has nothing extra about it. It is not like the other aspects that we are going to discuss in the next part.
Simple tense does not add any new information or anything fancy to the normal form. True to its name, simple tense is actually simple and the easiest of their forms, with very few rules.
Perfect Tense
Well, it is a little complicated to define perfect tense. This is mainly used to define actions that can be related to some other point in time, something that is completed or is still happening.
For instance, take the sentence, “She has danced since she was a child.” Here, the perfect tense shows that action happened continuously in the past and is still happening in the present.
But in contrast, if you consider the sentence, “She used to dance when she was a child,” the simple past tense shows that the action only happened in the past and has no relation to the present.
The perfect tense uses a conjugation of the auxiliary verb have along with the past participle form of the main verb.
Continuous Tense
The continuous tense, or the progressive tense, is used for ongoing actions or actions that happen just a moment before completion. For instance, “They are preparing all night for it.”
This sentence shows that it is going to take them all night to prepare for something before it is completely done. But make sure that you do not use continuous tense with stative verbs like need, want, have, and love.
The continuous tense uses a conjugation of the auxiliary verb ‘be’ along with the actual verb’s present participle or the ‘ing’ form.
Perfect Continuous Tense
In simple terms, when you combine the continuous and perfect tense, you make the perfect continuous tense. It is mostly used like the perfect tense, but it mostly describes any ongoing action that occurs over a certain period of time.
To construct the perfect continuous tense, you have to use a conjugation of the auxiliary verb form have, along with the auxiliary verb combined with the present participle form of the main verb.
Subtypes Of The Tenses
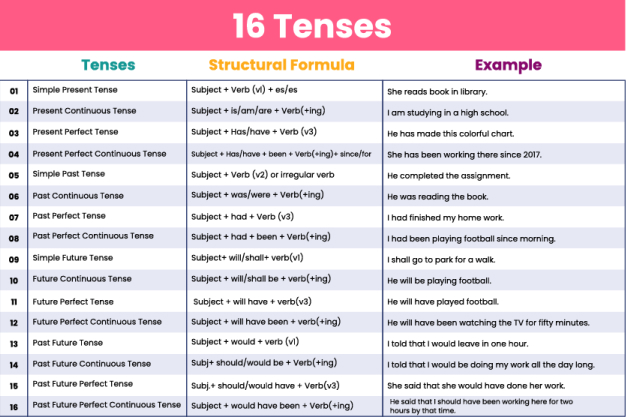
Well, if you thought it was the end of it, then you were wrong. There are still subtypes of tense, and those are equally important.
Past Continuous
The past continuous tense is mainly used to describe actions or events that have already happened in the past.
Structural formula: Subject + helping verb + verb +object
Examples
- I was playing in the backyard.
- She was sleeping after returning from school.
Past Perfect
The past perfect tense is mostly used for describing any event that happened before the completion of the action in the past.
Structured formula: Subject + had + verb + object
Examples
- They had met long before I went to college.
- She had never lived in Manhattan.
Past Perfect Continuous
The past perfect continuous tense shows any event or action that was started in the past and continues for another time or another action.
Structural formula: Subject + had been + verb (ing) + Object (optional) + time of action
Examples:
- They have been traveling for almost a month now.
- She had been preparing for almost a year for the job.
Present Continuous
This one is used to represent an ongoing event, action, or any condition that is still not finished.
Structural formula: Subject + helping verb (is / am/ are) + main verb (ing) + object
Examples:
- He is playing football.
- I’m teaching music.
Present Perfect
This one is used for describing any event or situation which has already happened and has immediate consequences.
Structural formula: Subject + helping verb (have/has) + verb (ed) + object
Examples:
- She has seen this movie twice.
- We have visited Las Vegas many times.
Present Perfect Continuous
This depicts a situation that has already started in the past and still continuing in the present.
Structural formula: Subject + helping verb (have/has) + been + verb (ing) + object (optional) + since / for + time duration + object
Examples:
- She has been teaching for several years now.
- They have been saving money.
Future Continuous
This tense is basically used for describing any ongoing action that will occur in the future.
Structural formula: Subject + shall/will be + verb (ing) + object
Examples:
- She will be coming to meet us next month.
- She will be leaving for New York tomorrow.
Future Perfect
This tense is for describing any action that will be completed between now and a given point in time in the future.
Structural formula: Subject + shall/will + have + verb (3rd form) + object
Examples:
- She will have finished her dinner before we reach there.
- He will have cleaned the entire house before he leaves for college.
Future Perfect Continuous
The future perfect continuous tense is used to focus on the time of the action before a particular time in the future.
Structural formula: Subject + shall/will + have been + verb (ing) + object (optional) + time instant
Examples:
- She will have been preparing hard before the exam.
- We will have been traveling for a while before they even started the journey.
Verb Tense Chart For Better Understanding
Let’s check a chart about the tenses in English for a better understanding of it.
| Past | Present | Future | |
| Simple | I went to college yesterday. | I go to college every day. | I will be going to college tomorrow. |
| Perfect | I had gone to college yesterday. | I have gone to college every day this week. | I shall have been gone to college. |
| Continuous | I was going to college when I met Bob. | I am going to college to meet Bob. | I will be going to college to meet Bob. |
| Perfect Continuous | I had been going to college since last year. | I have been going to college since last year. | This May, I will have been going to college for a year. |
Wrapping up!
Tense in English is the basic that you have to learn. There is no shortcut to this, and you have to learn this for effective communication. So, even to convey a message accurately or avoid basic grammar mistakes, you need to have a good grip on the knowledge, and for that, knowing the tense is a must.
